
Diving into the realm of Behavioral psychology approaches to habit formation, this introduction sets the stage for a deep exploration of how our behaviors shape our habits, with a focus on practical strategies and real-life examples.
Exploring the fundamental principles and applications of behavioral psychology in habit formation, this discussion aims to shed light on the intricate relationship between our behaviors and the habits we form.
Overview of Behavioral Psychology Approaches to Habit Formation

Behavioral psychology focuses on how behaviors are learned and can be changed through conditioning. When it comes to habit formation, this approach looks at how repeated behaviors become automatic responses over time.
Principles of Behavioral Psychology in Habit Formation
Behavioral psychology suggests that habits are formed through a process of reinforcement and repetition. When a behavior is consistently rewarded, it is more likely to be repeated in the future. This can be seen in everyday life, such as rewarding oneself with a treat after completing a workout, which reinforces the habit of exercising regularly.
Application of Behavioral Psychology in Forming New Habits
- Setting clear and achievable goals: By breaking down a larger habit into smaller, manageable steps, individuals can gradually build up to the desired behavior.
- Using positive reinforcement: Rewarding oneself for engaging in the desired behavior can help reinforce the habit and make it more likely to be repeated.
- Creating cues and triggers: Associating the new habit with specific cues or triggers, such as placing workout clothes by the bed to encourage morning exercise, can help prompt the behavior.
Examples of Behavioral Psychology Techniques in Changing Behaviors
- Token economy: Rewarding oneself with tokens or points for completing tasks or behaviors, which can then be exchanged for a desired reward, can motivate behavior change.
- Behavioral contracts: Setting up agreements with oneself or others to adhere to specific behaviors and consequences for not following through can help in establishing new habits.
- Modeling behavior: Observing and imitating the behaviors of others who exhibit the desired habit can serve as a powerful motivator for behavior change.
Conditioning and Habit Formation
Classical conditioning plays a crucial role in habit formation by associating a stimulus with a specific response. This process involves learning through the association of two stimuli, where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a natural response. Over time, this association strengthens, leading to the development of a habitual behavior.Operant conditioning, on the other hand, focuses on the consequences of behavior to shape future actions.
By using reinforcement and punishment, operant conditioning influences the likelihood of a behavior occurring again in the future. Habits can be formed or changed through the use of positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, positive punishment, or negative punishment.
Classical vs. Operant Conditioning in Habit Formation
In classical conditioning, behaviors are influenced by the pairing of stimuli, leading to an automatic response. This type of conditioning is more passive, as the individual does not actively engage in the learning process but rather responds to environmental cues. On the other hand, operant conditioning involves a more active participation from the individual, as behaviors are shaped based on the consequences that follow.
- Classical conditioning creates associations between stimuli and responses, leading to habitual behaviors triggered by specific cues.
- Operant conditioning focuses on the consequences of behaviors, reinforcing or punishing actions to shape future habits.
- Classical conditioning is more passive, while operant conditioning requires active engagement and decision-making from the individual.
- Both forms of conditioning play a role in habit formation, with classical conditioning establishing initial associations and operant conditioning shaping behaviors over time.
Rewards and Punishments in Habit Formation
In behavioral psychology, rewards play a crucial role in reinforcing habit formation. When a behavior is followed by a reward, the brain releases dopamine, which creates a sense of pleasure and satisfaction. This positive reinforcement strengthens the neural pathways associated with the behavior, making it more likely to be repeated in the future.
On the other hand, punishments can be effective in breaking unwanted habits by creating negative associations with certain behaviors. When a behavior leads to a punishment or an unpleasant consequence, the brain learns to avoid that behavior to prevent further negative outcomes. Punishments can help in extinguishing behaviors that are harmful or undesirable.
Rewards in Habit Formation
- Rewards can be used to encourage desired behaviors and make them more likely to occur in the future.
- Examples of rewards include praise, treats, or other incentives that provide a sense of satisfaction and pleasure.
- By consistently rewarding a behavior, individuals are motivated to continue engaging in that behavior to experience the positive outcomes associated with it.
Punishments in Breaking Unwanted Habits
- Punishments can help in reducing or eliminating behaviors that are harmful, undesirable, or have negative consequences.
- Examples of punishments include timeouts, fines, or loss of privileges that deter individuals from engaging in certain behaviors.
- When behaviors lead to punishments, individuals are more likely to avoid those behaviors to prevent further negative outcomes.
Environmental Cues and Habit Formation
Environmental cues play a crucial role in triggering habits as they act as reminders or signals that prompt specific behaviors. These cues can be anything from physical objects to time of day or even emotions.
Significance of Environmental Cues
Environmental cues help individuals associate specific behaviors with certain contexts, making it easier to repeat those behaviors over time. For example, seeing your running shoes by the door can remind you to go for a run every morning.
Modifying Environments for Habit Formation
Individuals can modify their environments to support habit formation by strategically placing cues that encourage the desired behavior. This can involve removing obstacles that hinder the habit or adding visual reminders to reinforce it.
Strategies for Creating a Conducive Environment
- Avoiding temptations: Keep unhealthy snacks out of sight to reduce the temptation to indulge.
- Setting up reminders: Use sticky notes or alarms to remind yourself to engage in the desired habit.
- Designating a specific space: Create a designated area for the habit to signal that it’s time to engage in the behavior.
- Creating a routine: Establish a consistent routine that includes the habit to reinforce its importance.
- Seeking social support: Surround yourself with individuals who encourage and support the habit you’re trying to form.
Habit Loop and Behavioral Psychology
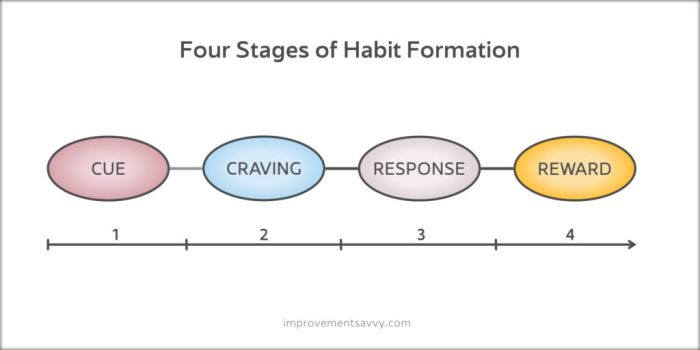
In behavioral psychology, the habit loop refers to a three-step process that governs habitual behavior. This loop consists of a cue, a routine, and a reward. Understanding this loop is crucial in shaping and changing habits effectively.
Components of the Habit Loop
The habit loop is comprised of three main components:
- Cue: This is the trigger that initiates the habit. It can be a specific time of day, a particular emotion, a location, or any other stimulus that prompts the behavior.
- Routine: The routine is the behavior or action that follows the cue. It is the habitual response to the trigger, often performed automatically and without much conscious thought.
- Reward: The reward is the positive reinforcement that follows the routine. It serves to reinforce the habit loop, making it more likely to be repeated in the future.
Benefits of Understanding the Habit Loop
By understanding the habit loop, individuals can identify the cues that trigger unwanted habits, modify the routines to more positive behaviors, and ensure that there is a rewarding outcome. This awareness allows for intentional habit formation and change, leading to lasting behavioral adjustments.
Real-Life Examples of the Habit Loop
One common example of the habit loop is the habit of snacking while watching TV. The cue might be sitting down in front of the television, the routine is reaching for a bag of chips, and the reward is the satisfying crunch and taste of the snack. Over time, this loop becomes ingrained, and the behavior is repeated whenever the cue is present.Another example is the habit of checking social media constantly.
The cue could be boredom or the desire for connection, the routine is scrolling through feeds, and the reward is the temporary distraction or sense of connection. Understanding this loop can help individuals break free from excessive social media use by identifying alternative routines and rewards.Overall, the habit loop provides valuable insights into the psychology of habit formation and change, highlighting the power of cues, routines, and rewards in shaping behavior.
Role of Repetition and Consistency in Habit Formation
Repetition and consistency are key elements in the process of habit formation, as they help solidify new behaviors and make them automatic responses in our daily lives.
Importance of Repetition in Habit Formation
Repetition plays a crucial role in habit formation by reinforcing the neural pathways associated with the behavior we are trying to establish. When we repeat a behavior consistently, these neural connections become stronger, making it easier for us to perform the action without much conscious effort.
- Repetition helps in encoding the habit into our brain’s circuitry, making it more automatic over time.
- Consistent repetition creates a sense of familiarity and comfort with the habit, making it feel more natural to engage in.
- Repetition also helps in overcoming initial resistance or inertia towards the new habit, as the more we do something, the more it becomes a part of our routine.
- By repeating the behavior regularly, we are essentially training our brains to prioritize and execute the habit efficiently.
Role of Consistency in Habit Formation
Consistency is equally important in habit formation, as it establishes a pattern that our brains can rely on and predict. When we are consistent in our efforts to practice a new habit, it reinforces the behavioral loop and makes it easier for our brains to recognize and respond to cues that trigger the habit.
- Consistency helps in building momentum and momentum is key to sustaining a habit over the long term.
- When we are consistent in our actions, our brains start to anticipate the habit at specific times or in certain situations, making it more likely to stick.
- Consistency also helps in creating a sense of accountability and commitment to the habit, as we are more likely to follow through when we have established a routine.
- By being consistent, we are essentially creating a stable environment for the new habit to thrive and become ingrained in our daily lives.
Behavior Change Techniques in Online Education
Utilizing behavioral psychology approaches in online education can significantly impact students’ habit formation and learning outcomes. By understanding how reinforcement and feedback shape behaviors, educators can implement effective behavior change techniques to enhance student engagement and success.
Role of Reinforcement and Feedback in Online Learning
Reinforcement and feedback play a crucial role in shaping behaviors in online learning environments. Positive reinforcement, such as rewards or praise, can motivate students to engage actively with course materials and complete assignments. On the other hand, constructive feedback helps students understand their progress, identify areas for improvement, and adjust their learning strategies accordingly.
Examples of Behavior Change Techniques in Online Education
- Goal Setting: Encouraging students to set specific, achievable goals can promote a sense of accomplishment and motivation to progress in their learning journey.
- Progress Tracking: Providing students with visual progress indicators, such as progress bars or completion percentages, can help them monitor their advancement and stay motivated to reach their objectives.
- Social Support: Creating opportunities for peer interaction and collaboration can foster a sense of community and support among students, enhancing their engagement and learning experience.
- Adaptive Learning: Implementing adaptive learning technologies that personalize the learning experience based on individual performance and preferences can optimize student engagement and knowledge retention.
- Gamification: Introducing game elements, such as points, badges, or leaderboards, into the online learning platform can make learning more interactive and enjoyable, motivating students to actively participate and achieve learning goals.
Incorporating Behavioral Psychology in Special Education
When it comes to special education, incorporating behavioral psychology strategies is essential to support students with special needs in their learning and development. By understanding how behavior is influenced and modified, educators can create individualized behavior plans that cater to the unique requirements of each student.
Adapting Behavioral Psychology Strategies for Students with Special Needs
Special education settings require a tailored approach to address the specific challenges and strengths of students with disabilities. Behavioral psychology strategies such as positive reinforcement, prompting, shaping, and modeling can be adapted to meet the diverse needs of students with special education requirements. These strategies focus on reinforcing positive behaviors and teaching new skills in a structured and supportive environment.
Importance of Individualized Behavior Plans
Individualized behavior plans based on behavioral psychology principles are crucial in special education as they provide a roadmap for addressing behavioral challenges and promoting positive outcomes. These plans take into account the unique needs, abilities, and preferences of each student, ensuring that interventions are targeted and effective. By tailoring strategies to individual students, educators can create a supportive and inclusive learning environment that maximizes student success.
Success Stories in Special Education
There are numerous success stories and case studies where behavioral psychology approaches have had a positive impact on students with special education needs. For example, implementing a reinforcement schedule to encourage desired behaviors, using visual supports to enhance communication skills, or teaching self-regulation techniques to improve emotional regulation have all shown significant improvements in student outcomes. By applying evidence-based practices rooted in behavioral psychology, educators can empower students with special needs to reach their full potential.
Standardized Tests Preparation and Behavioral Psychology
Behavioral psychology techniques can be highly effective in improving performance in standardized test preparation. By understanding how habits are formed and utilizing conditioning principles, students can enhance their study habits and manage test anxiety more effectively.
Strategies for Managing Test Anxiety
- Identify triggers: Recognize what situations or thoughts trigger anxiety during test preparation.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Incorporate deep breathing exercises or mindfulness practices to reduce stress levels.
- Positive self-talk: Encourage positive affirmations and self-belief to boost confidence before and during exams.
- Break tasks into smaller steps: Create a study schedule with manageable tasks to prevent feeling overwhelmed.
Enhancing Study Habits using Behavioral Psychology Principles
- Reward system: Implement a reward system for completing study sessions or achieving study goals to reinforce positive behavior.
- Consistency: Establish a consistent study routine to build a habit of studying regularly.
- Environmental cues: Create a conducive study environment with minimal distractions to enhance focus and concentration.
- Goal setting: Set specific, achievable study goals to keep motivation high and track progress effectively.
Incorporating Behavioral Psychology Approaches in Standardized Test Preparation
- Utilize spaced repetition: Implement spaced repetition techniques to improve retention of material and enhance long-term memory.
- Practice active recall: Engage in active recall methods such as flashcards or practice quizzes to reinforce learning and improve recall during exams.
- Peer accountability: Form study groups or study partners to hold each other accountable and maintain motivation throughout the preparation process.
- Feedback mechanism: Seek feedback from teachers or mentors to identify areas of improvement and adjust study strategies accordingly.
Behavioral Psychology Strategies in Survival and Emergency Situations
In survival and emergency situations, understanding behavioral psychology can greatly impact decision-making and actions taken. Behavioral psychology theories provide insights into stress responses and coping mechanisms that can be crucial for increasing preparedness and resilience in such scenarios.
Role of Stress Response and Coping Mechanisms
In survival situations, individuals may experience high levels of stress, which can impair rational decision-making. Understanding how stress affects behavior and learning effective coping mechanisms can significantly improve outcomes. Behavioral psychology emphasizes the importance of recognizing stress triggers, managing emotions, and developing adaptive responses to challenging situations.
- Identifying Stress Triggers: By identifying specific triggers that lead to stress, individuals can proactively address these factors and reduce their impact on decision-making.
- Emotion Regulation: Techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and positive self-talk can help regulate emotions and prevent impulsive reactions in high-pressure situations.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Behavioral psychology encourages the development of problem-solving skills to tackle challenges systematically and efficiently, even under duress.
- Social Support: Building a support network and seeking help from others can enhance resilience and provide valuable resources during emergencies.
Applying Behavioral Psychology Strategies in Survival Scenarios
When faced with survival situations, individuals can benefit from applying behavioral psychology strategies to enhance their chances of survival and successful outcomes.
By understanding the psychological principles that govern behavior, individuals can make informed decisions, adapt quickly to changing circumstances, and maintain a positive mindset in challenging environments.
Teaching Strategies Rooted in Behavioral Psychology
Behavioral psychology principles can be effectively integrated into teaching strategies to foster positive behaviors and enhance learning outcomes in students. By understanding how behavior is influenced by environmental factors, teachers can implement techniques that promote desirable behaviors and discourage negative ones.
Use of Reinforcement, Modeling, and Feedback
Incorporating reinforcement, modeling, and feedback mechanisms in the classroom setting can significantly impact student behavior. Reinforcement involves rewarding desired behaviors to increase the likelihood of their repetition. Teachers can utilize positive reinforcement such as praise, rewards, or privileges to reinforce good behavior. Modeling involves demonstrating the desired behavior for students to observe and imitate. By showcasing positive behaviors, teachers can encourage students to emulate them.
Feedback plays a crucial role in providing information about the consequences of behavior, allowing students to adjust their actions accordingly.
- Teachers can utilize positive reinforcement techniques like verbal praise, stickers, or extra privileges to reinforce positive behaviors such as completing assignments on time or participating actively in class discussions.
- Modeling behaviors by displaying respect, empathy, and enthusiasm in interactions with students can set a positive example for students to follow.
- Providing timely and constructive feedback on student performance can help students understand the impact of their actions and make necessary adjustments to improve.
Effective Teaching Strategies Aligned with Behavioral Psychology Concepts
Implementing behavioral psychology concepts in teaching strategies can lead to improved behavior management and enhanced learning experiences for students. By creating a structured and supportive learning environment, teachers can promote positive behaviors and academic success.
- Setting clear expectations and consistent routines can help establish a sense of predictability and security for students, reducing disruptive behaviors.
- Using visual aids, such as charts or diagrams, can assist in reinforcing concepts and providing visual cues for desired behaviors.
- Implementing group reinforcement strategies, where students are rewarded collectively for achieving set goals, can foster a sense of teamwork and motivation among students.
Behavioral Psychology in Education and Training Programs
Integrating behavioral psychology concepts into education and training programs can significantly enhance the effectiveness of learning experiences. By understanding behavior change theories, educators and trainers can optimize learning outcomes in various educational settings.
Incorporating Behavioral Psychology in Curriculum Development
When designing curriculum, it is essential to consider the principles of behavioral psychology to create engaging and effective learning experiences. Incorporating elements such as rewards, punishments, and environmental cues can help reinforce desired behaviors and facilitate habit formation among learners.
Training Delivery Methods Rooted in Behavioral Psychology
- Utilizing reinforcement techniques: Implementing positive reinforcement strategies can motivate learners to engage actively in training programs and maintain consistent participation.
- Behavioral modeling: Demonstrating desired behaviors and providing opportunities for learners to mimic those behaviors can enhance skill acquisition and retention.
- Feedback mechanisms: Offering timely and constructive feedback can help learners track their progress, identify areas for improvement, and adjust their behavior accordingly.
Background of Behavioral Psychology in Education
Behavioral psychology has played a significant role in shaping educational practices and strategies over the years. By understanding how behaviors are learned and influenced, educators can effectively design interventions to improve learning outcomes and student behavior in the classroom.
Historical Development of Behavioral Psychology in Education
- Behavioral psychology traces its roots back to the work of Ivan Pavlov and his experiments on classical conditioning with dogs in the late 19th century.
- B.F. Skinner, a prominent behaviorist, further developed the principles of operant conditioning, emphasizing the role of reinforcement and punishment in shaping behavior.
- The application of behavioral psychology in education gained momentum in the mid-20th century, with a focus on behavior modification techniques to address learning difficulties and behavioral challenges in students.
Key Theorists and Studies in Behavioral Psychology and Education
- One of the key theorists in the field is B.F. Skinner, whose work on operant conditioning has had a profound impact on educational practices.
- The Bobo doll experiment conducted by Albert Bandura highlighted the role of observational learning in behavior acquisition, influencing teaching methods that emphasize modeling and imitation.
- Research studies on behavioral interventions in special education have provided valuable insights into how behavior modification techniques can effectively support students with learning disabilities.
Evolution of Behavioral Psychology in Educational Settings
- Over time, behavioral psychology has evolved to encompass a broader range of strategies and interventions aimed at promoting positive behaviors and academic success in students.
- The integration of technology and data-driven approaches in education has allowed for more personalized and adaptive learning experiences based on behavioral principles.
- Current educational practices often incorporate elements of behavioral psychology, such as positive reinforcement, behavior contracts, and self-regulation strategies, to foster a conducive learning environment.
Recommended Books on Behavioral Psychology in Education
In the field of education, understanding behavioral psychology can be crucial for effective teaching and learning strategies. Below is a list of essential books that delve into the intersection of behavioral psychology and education, providing valuable insights for educators, psychologists, or individuals interested in the subject.
1. “Teaching with Love & Logic” by Jim Fay and David Funk
- This book emphasizes the importance of building positive teacher-student relationships based on mutual respect and responsibility.
- It offers practical strategies for managing classroom behavior and promoting student autonomy through logical consequences.
- Valuable for educators looking to implement positive discipline techniques and create a supportive learning environment.
2. “The Power of Positive Parenting
Transforming the Lives of Children, Parents, and Teachers” by Dr. Glenn Latham
- Dr. Latham explores the impact of positive reinforcement and effective communication on children’s behavior and academic performance.
- The book provides evidence-based strategies for parents and educators to foster positive relationships and encourage desirable behaviors.
- Essential reading for those seeking to understand the role of positive parenting in shaping children’s cognitive and emotional development.
3. “Behavioral Interventions in Schools
Evidence-Based Positive Strategies” by Angela J. Ardoin and Rosemary B. Mennuti
- This book offers a comprehensive overview of evidence-based practices for addressing behavioral challenges in school settings.
- It covers a range of behavioral interventions, including functional behavior assessments, positive behavior support, and social-emotional learning programs.
- Recommended for educators and school professionals looking to implement effective strategies to support students with diverse behavioral needs.
4. “The ABCs of Behavior Analysis” by Juan Rosai
- Dr. Rosai provides a practical guide to understanding the principles of behavior analysis and their application in educational settings.
- The book covers topics such as reinforcement, punishment, shaping, and fading techniques to modify behavior effectively.
- Useful for educators and behavior specialists seeking to enhance their knowledge of behavior analysis and its impact on student learning outcomes.
In conclusion, the journey through Behavioral psychology approaches to habit formation unveils the power of understanding our behaviors in shaping the habits that define us, offering valuable insights and actionable steps for personal growth and behavior change.
Quick FAQs
How can environmental cues impact habit formation?
Environmental cues play a crucial role in triggering habits by creating associations in our minds between certain actions and specific environments. Modifying our surroundings can support habit formation by providing consistent prompts for desired behaviors.
What is the significance of the habit loop in behavioral psychology?
The habit loop consists of cue, routine, and reward, forming a cycle that influences our habit formation. Understanding this loop can help individuals identify triggers for behaviors, modify routines, and create new habits effectively.
How can teachers incorporate behavioral psychology in classroom settings?
Teachers can leverage principles like reinforcement, modeling, and feedback to encourage positive behaviors in students. By aligning teaching strategies with behavioral psychology concepts, educators can create a conducive learning environment that fosters behavior management and enhances student learning.





