
Delving into the variances between psychiatry and clinical psychology, this exploration uncovers the fundamental disparities that shape these distinct realms of mental health.
From the core focus areas to the treatment approaches, the following breakdown illuminates the unique paths pursued by psychiatrists and clinical psychologists.
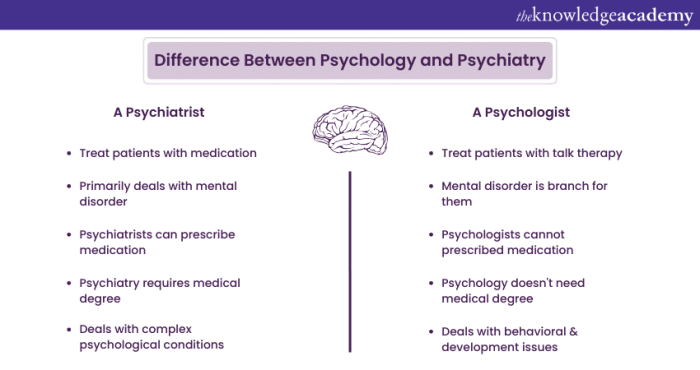
Differences between psychiatry and clinical psychology
Psychiatry and clinical psychology are two distinct fields within the mental health profession, each with its own focus and approach to treatment. Here, we will delve into the core differences between psychiatry and clinical psychology, including their focus areas, educational paths, and treatment approaches.
Core Focus Areas
Psychiatry is a branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illnesses. Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication and often work with patients who have severe or complex mental health issues. On the other hand, clinical psychology focuses on assessing, diagnosing, and treating emotional and behavioral disorders using psychotherapy and counseling. Clinical psychologists work with individuals, couples, families, and groups to address a wide range of mental health concerns.
Educational Paths
To become a psychiatrist, individuals must complete medical school, followed by a residency in psychiatry. This involves several years of clinical training in hospitals and mental health facilities. In contrast, clinical psychologists typically earn a doctoral degree in psychology (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) with a specialization in clinical psychology. They also undergo supervised clinical training and may pursue further certification or licensure depending on their location.
Treatment Approaches
Psychiatrists often use a combination of medication management and psychotherapy to treat mental health disorders. They focus on the biological aspects of mental illness and may prescribe medications to address chemical imbalances in the brain. Clinical psychologists, on the other hand, primarily use talk therapy and behavioral interventions to help individuals overcome emotional difficulties and improve their mental well-being. They emphasize the importance of understanding the underlying psychological factors contributing to a person’s symptoms.
Online Education
Online education in the field of psychology offers numerous benefits, such as flexibility in scheduling, accessibility to a broader range of students, and the ability to learn at one’s own pace. It also allows for the integration of multimedia resources and collaborative tools to enhance the learning experience.
Benefits of Online Education in Psychology
- Flexibility in scheduling: Students can access lectures and course materials at any time, allowing them to balance their studies with other commitments.
- Accessibility: Online education eliminates geographical barriers, making it easier for students from different locations to enroll in psychology programs.
- Enhanced learning experience: The use of multimedia resources, online discussions, and virtual simulations can engage students and facilitate a deeper understanding of psychological concepts.
- Cost-effective: Online education often requires fewer resources than traditional classroom settings, making it a more affordable option for both students and institutions.
Challenges in Transitioning to Online Teaching
- Technical difficulties: Educators may face challenges in adapting to new technology platforms and troubleshooting issues that arise during online classes.
- Lack of personal interaction: Online education can sometimes lead to a sense of isolation for students and instructors, impacting the overall learning experience.
- Maintaining engagement: Keeping students engaged in online courses and ensuring active participation can be more challenging compared to face-to-face interactions.
- Assessment methods: Developing effective methods for evaluating student performance and ensuring academic integrity in an online setting can be complex.
Effective Online Education Tools and Platforms in Psychology Programs
- Blackboard: A popular learning management system that allows educators to create online courses, deliver content, and assess student learning.
- Coursera: An online platform that offers a wide range of psychology courses taught by experts from universities around the world.
- Kahoot!: A game-based learning platform that can be used to create interactive quizzes and polls to assess student understanding of psychological concepts.
- Zoom: A video conferencing tool that enables educators to conduct live lectures, discussions, and virtual office hours with students.
Psychology
Psychology plays a crucial role in understanding human behavior, emotions, and cognitive processes. It helps us explore the complexities of the mind and behavior, providing valuable insights into how individuals think, feel, and act in various situations.
Branches of Psychology
- Clinical Psychology: Focuses on diagnosing and treating mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
- Cognitive Psychology: Studies mental processes such as perception, memory, and problem-solving.
- Developmental Psychology: Examines human growth and development across the lifespan.
- Social Psychology: Investigates how individuals are influenced by others and how they interact in social settings.
Role of Psychology in Mental Health
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Psychologists use various techniques to assess and treat mental health issues, providing therapy and interventions to improve well-being.
- Prevention: Psychology helps in identifying risk factors for mental health problems and implementing preventive measures to promote mental wellness.
- Educational Support: Psychologists work in schools to address behavioral issues, learning disabilities, and emotional concerns among students.
- Research: Psychological research contributes to the development of effective interventions and therapies for mental health conditions.
Special Education
Special education refers to the tailored educational programs and support services designed to meet the unique needs of students with disabilities or special learning requirements. It aims to provide these individuals with equal opportunities for learning and development.
Key Principles and Strategies in Special Education
- Individualized Education Plan (IEP): A personalized roadmap outlining the student’s specific learning goals, services, and accommodations.
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): Implementing flexible teaching methods and materials to cater to diverse learning styles and abilities.
- Collaborative Approach: Involving parents, teachers, therapists, and specialists to create a supportive learning environment for the student.
- Differentiated Instruction: Adapting teaching techniques and content to suit the individual needs and strengths of each student.
Role of Special Education Teachers
- Assessment and Evaluation: Identifying students’ strengths and challenges to develop appropriate strategies and interventions.
- Instruction and Support: Providing specialized instruction, accommodations, and assistive technologies to help students achieve their learning goals.
- Advocacy: Acting as a voice for students with disabilities, ensuring they receive the necessary resources and support for their education.
Assistive Technologies in Special Education
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices: Tools that help nonverbal students communicate through speech output or symbols.
- Text-to-Speech Software: Assisting students with reading difficulties by converting written text into spoken words.
- Visual Aids: Including graphic organizers, magnification tools, and color-coded systems to support students with visual impairments or processing disorders.
Standardized Tests
Standardized testing has been a long-standing practice in the education system, aiming to provide a measure of student performance on a uniform scale. While these tests have their advantages in terms of providing a standardized assessment tool, they also come with their fair share of drawbacks.
Pros and Cons of Standardized Testing
- Pros:
- Provides a consistent measure of student performance
- Allows for comparison of student achievement across schools and districts
- Helps identify areas for improvement in curriculum and teaching methods
- Cons:
- May lead to teaching to the test rather than fostering critical thinking skills
- Can create undue stress and anxiety for students
- May not accurately reflect a student’s true abilities or potential
Impact of Standardized Tests on Student Learning Outcomes
Standardized tests have a significant impact on student learning outcomes, as they often influence the curriculum taught in schools. Schools may prioritize subjects or topics that are heavily tested, potentially neglecting other important areas of learning. Additionally, the pressure to perform well on these tests can affect students’ mental health and overall well-being.
Types of Standardized Tests
There are various types of standardized tests used to assess academic performance, each serving a specific purpose and target audience.
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| State Standardized Tests | Measure student proficiency in state-mandated subjects |
| College Entrance Exams | Assess students’ readiness for higher education |
| International Assessments | Compare student performance on a global scale |
Survival and Emergency

Survival and emergency training are crucial components of educational programs as they equip students with the necessary skills to handle unexpected situations and protect themselves and others in times of crisis. By incorporating survival and emergency training into the curriculum, schools can empower students to act confidently and responsibly during emergencies.
Importance of Survival Skills Training
It is essential to include survival skills training in educational programs to ensure that students are prepared to face various emergency situations. Some examples of survival skills that can be taught in schools include:
- First aid techniques such as CPR and wound care
- Fire safety and evacuation procedures
- Basic survival skills like building shelters and finding sources of food and water
- Emergency communication strategies
Role of Educators in Emergency Preparedness
Educators play a vital role in preparing students for emergency situations by providing them with the knowledge and skills needed to respond effectively. Teachers can conduct drills, simulations, and training sessions to familiarize students with emergency protocols and procedures. By instilling a sense of preparedness and resilience in students, educators can help create a safer learning environment for everyone.
Teaching
Effective teaching is crucial for engaging students in the learning process and promoting their overall academic success. By utilizing various strategies and creating a positive and inclusive learning environment, educators can enhance student participation and motivation in the classroom.
Engaging Strategies
- Utilize interactive activities such as group discussions, hands-on experiments, and multimedia presentations to keep students actively involved in the learning process.
- Incorporate real-life examples and case studies to make the content more relatable and applicable to students’ lives.
- Provide opportunities for students to collaborate with their peers through group projects and presentations, fostering teamwork and communication skills.
- Offer a variety of assessment methods such as quizzes, projects, and class participation to cater to different learning styles and keep students engaged.
Creating a Positive Environment
- Establish clear expectations and guidelines for behavior in the classroom to create a safe and respectful learning environment.
- Show empathy and understanding towards students’ diverse backgrounds and learning needs, promoting inclusivity and acceptance among peers.
- Encourage open communication and feedback, allowing students to voice their opinions and concerns without fear of judgment or retribution.
- Celebrate students’ achievements and progress, providing positive reinforcement to boost their confidence and motivation.
Promoting Student Participation
- Encourage active participation through discussions, debates, and group activities that require students to engage with the material and each other.
- Provide opportunities for students to take on leadership roles within the classroom, promoting autonomy and responsibility for their own learning.
- Offer constructive feedback and praise to acknowledge students’ contributions and efforts, motivating them to continue participating and striving for excellence.
- Use technology and multimedia resources to enhance student engagement and interest in the subject matter, making learning more interactive and dynamic.
Education and Training
Continuous education and training are crucial for educators to stay updated with the latest teaching techniques, educational trends, and advancements in their field. This ongoing professional development ensures that educators are equipped to meet the diverse needs of their students and create an engaging learning environment.
Impact of Professional Development on Teaching Practices
Professional development plays a significant role in enhancing teaching practices by providing educators with new strategies, tools, and resources to improve student learning outcomes. It helps teachers reflect on their teaching methods, collaborate with peers, and integrate innovative approaches into their lessons. By participating in professional development opportunities, educators can enhance their skills, knowledge, and effectiveness in the classroom.
- Workshops: Workshops offer hands-on training and practical strategies for educators to implement in their classrooms. Topics may include classroom management, differentiated instruction, technology integration, and assessment techniques.
- Seminars: Seminars provide a platform for educators to engage with experts in the field, discuss current educational issues, and explore new research-based practices. Seminars cover a wide range of topics such as literacy development, special education, STEM education, and social-emotional learning.
- Conferences: Educational conferences bring together educators from various backgrounds to share best practices, research findings, and innovative ideas. Educators can attend keynote presentations, breakout sessions, and networking events to gain insights and inspiration for their teaching.
Education Article
When crafting a well-researched education article, it is essential to include the following components:
Essential Components of a Well-Researched Education Article
- Introduction that clearly Artikels the main topic of the article and provides context for the reader.
- Literature review that summarizes existing research on the subject and highlights gaps in knowledge.
- Methodology section detailing how the research was conducted, including participant demographics and data collection methods.
- Results section presenting the findings of the study in a clear and organized manner.
- Discussion section that interprets the results, relates them to existing literature, and offers implications for practice.
Importance of Citing Sources and Maintaining Academic Integrity
Citing sources is crucial in educational writing to give credit to the original authors, provide evidence for claims made in the article, and allow readers to delve deeper into the topic. Maintaining academic integrity ensures that the work is honest, trustworthy, and respects intellectual property rights.
Tips for Structuring and Formatting an Education Article for Publication
- Use clear headings and subheadings to organize the content and guide the reader through the article.
- Follow the required formatting style (e.g., APA, MLA) for citations, references, and overall layout.
- Include tables, figures, or graphs to visually represent data and enhance understanding.
- Proofread the article for grammar, spelling, and formatting errors before submission.
- Consider the target audience and tailor the language and tone of the article accordingly.
Education Background
One’s educational background plays a crucial role in shaping their career path, especially in the field of education. It influences the knowledge and skills individuals bring to their roles as educators and can impact their teaching approaches.
Role of Academic Qualifications
Academic qualifications serve as a foundation for educators, providing them with the necessary theoretical knowledge and practical skills to excel in their profession. They demonstrate a commitment to continuous learning and professional development, which is essential in the dynamic field of education.
Contribution of Different Educational Backgrounds
- Teachers with a background in psychology may have a better understanding of student behavior and learning processes, allowing them to tailor their teaching methods to individual needs.
- Educators with a special education background bring expertise in supporting students with diverse learning needs, ensuring an inclusive and accessible learning environment for all.
- Those with training in standardized tests can effectively assess student progress and tailor instruction to meet specific learning goals.
- Individuals with a background in survival and emergency training may incorporate valuable life skills and crisis management techniques into their teaching practices.
Education Book
Education books play a crucial role in providing valuable resources for both educators and students. They offer in-depth knowledge, practical strategies, and innovative ideas to enhance teaching and learning experiences.
These books have a significant impact on teaching practices by introducing new methodologies, approaches, and concepts that can be implemented in the classroom. Educators can gain insights into effective instructional techniques, classroom management strategies, and ways to cater to diverse learning needs.
Benefits of Using Educational Books
- Provide comprehensive information on educational theories and practices.
- Offer practical tips and strategies for improving teaching effectiveness.
- Enhance professional development and continuous learning for educators.
- Help students deepen their understanding of academic subjects and develop critical thinking skills.
Impact of Educational Literature on Teaching Practices
- Encourages educators to reflect on their teaching methods and adapt to new approaches.
- Promotes lifelong learning and professional growth among teachers.
- Fosters a culture of innovation and creativity in the field of education.
- Empowers educators to create engaging and inclusive learning environments.
Must-Read Educational Books for Educators and Students
- “The First Days of School: How to Be an Effective Teacher” by Harry K. Wong and Rosemary T. Wong
- “Teach Like a Champion: 49 Techniques that Put Students on the Path to College” by Doug Lemov
- “Mindset: The New Psychology of Success” by Carol S. Dweck
- “Pedagogy of the Oppressed” by Paulo Freire
As we conclude this discussion on the dichotomy between psychiatry and clinical psychology, it becomes evident that while both fields share a common goal of mental well-being, their methods and approaches diverge significantly, offering a rich tapestry of options for those seeking mental health support.
FAQ Summary
What are the primary differences in focus between psychiatry and clinical psychology?
Psychiatry deals with diagnosing and treating mental illnesses using medication, while clinical psychology focuses on therapy and counseling without prescription drugs.
What educational paths are required for a career in psychiatry versus clinical psychology?
Psychiatrists need to attend medical school and complete a residency, whereas clinical psychologists typically pursue a doctoral degree in psychology.
What are some common treatment approaches used by psychiatrists and clinical psychologists?
Psychiatrists often utilize medication management, while clinical psychologists employ various therapeutic modalities such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and psychoanalysis.





